GLS-ODT-C-NS and CN
The GLS-ODT-C-NS is a ceiling-mounted occupancy sensor designed to provide coverage for areas up to 2,000 square feet. The sensor utilizes both passive infrared (PIR) and ultrasonic (US) motion sensors to allow reliable motion detection. The GLS-ODT-C-NS can be used in standalone applications when paired with a GLPP, GLPAC, or GL-IPAC.
Note on GLS-ODT-C-NS and GLS-ODT-C-CN Power Draw
The listed power draw for GLS-ODT-C-NS and CN sensors is 45mA at 24VDC, however Chief Integrations' testing with shipped hardware shows the real-world power draw to be closer to 60mA. While GLPP modules are able to provide 150mA at 24VDC for sensors, this is insufficient for real-world applications involving more than two GLS-ODT-C-NS occupancy sensors.
As such, Chief Integrations recommends adding a GLA-TR-100 or other external power supply if more than two sensors are required to be added to one GLPP.
Detailed Analysis
The below measurements were taken with GLS-ODT-C-NS attached to a GLPP-1DIMFLV2CN-PM with ~1’ of wire using a Pokit portable oscilloscope in line to capture the current. The initial soft start (~270ms) is followed by full operation which draws ~60mA. 60mA average consumption is fairly stable for the remainder of the sensor’s runtime. PIR, US A and B are enabled as are the LEDs on this unit. Turning off some of those functions may reduce the current consumption but we have not measured them. Similar measurements were obtained with a Fluke 189 DMM so we know this Pokit capture is accurate. Alternative measurements were taken with an HP 6632A DC power supply as the 24VDC power source and similar readings were produced and confirmed by the power supply’s internal meter.
Note, a similar test has been done on a GLA-IR-QUATTRO-HD-COM1-24. These sensors are listed as requiring 32mA at 24VDC, however testing shows that the sensors actually draw ~60mA on startup before dropping to 20mA steady state within 50ms.
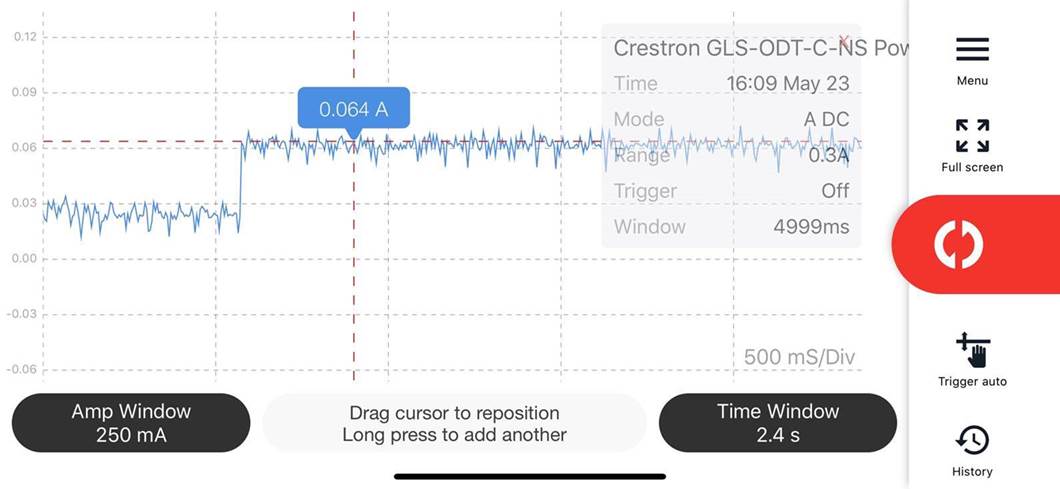
GLS-ODT-C-NS current draw readings.
